In the realm of materials science and electrochemical engineering, Titanium Electrode Wire represents a versatile and critical component. This term refers to titanium wire specifically designed for or used in electrochemical electrode systems, as well as other applications leveraging titanium’s unique properties in a wire form factor. Combining the inherent advantages of titanium with specific coatings or insulations, titanium electrode wire is essential in diverse fields from industrial processes to laboratory research.
This guide explores the different types of titanium wire relevant to electrode applications, their key properties, common uses, and technical specifications.
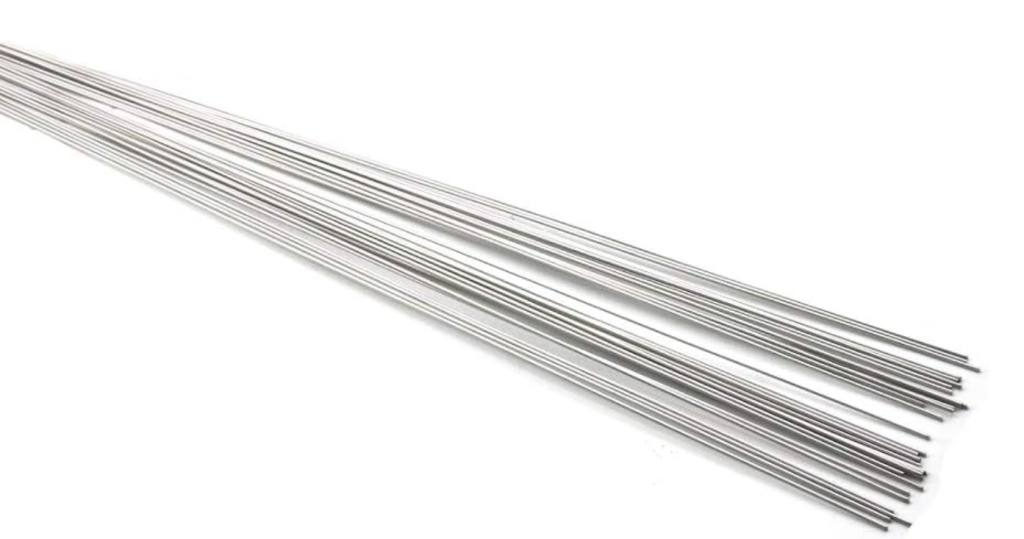

Understanding Titanium Wire (The Base Material)
At the heart of Titanium Electrode Wire is pure titanium or a titanium alloy wire.
- Material: Typically made from commercially pure titanium grades such as Grade 1 (most ductile) or Grade 2 (most common), offering an excellent balance of strength and formability. Alloys like Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), Grade 7, or Grade 12 are used when higher strength, different corrosion resistance, or specific properties are needed.
- Properties: Titanium wire inherits titanium’s core advantages:
- Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: Highly resistant to corrosion in oxidizing environments, chlorides, acids, and alkalis due to the rapid formation of a passive oxide layer.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Lighter than steel but significantly stronger than aluminum alloys.
- Biocompatibility: Pure titanium is non-toxic and compatible with biological tissues.
- Good Conductivity: Sufficient electrical conductivity for many applications, though surface oxides can limit it in some electrochemical contexts, necessitating coatings.
- General Uses: Beyond specific electrode uses, pure titanium wire is widely used for:
- Chemical processing and anodizing fixtures (hanging or tying parts undergoing treatment).
- TIG welding rods for joining titanium and its alloys in aerospace, medical, marine, and industrial fabrication.
- Various structural and conductive components in harsh environments.
- Specifications: Available in a wide range of diameters, typically from 0.03 mm (fine wire) up to 6 mm or more (rods). Conforms to industry standards like ASTM B863 (for titanium and titanium alloy wire) and AWS A5.16 (for titanium and titanium alloy welding rods).

Key Types of Titanium Electrode Wire
While pure titanium wire itself can serve as an electrode or electrode component, specific coatings or insulations create specialized types of Titanium Electrode Wire for different functions:
Platinum Coated Titanium Wire Electrode:
- Description: A titanium wire substrate precisely coated with a thin, adherent layer of pure platinum metal (Pt), typically 0.1 to 20 microns thick.
- Unique Feature: Combines titanium’s corrosion resistance with platinum’s superior catalytic activity and high electrical conductivity.
- Applications: Used as miniature or auxiliary anodes/working electrodes in:
- Electroplating baths (especially for precious metals and hard chrome plating).
- Electrochemical sensing.
- Electrosynthesis.
- Electrodialysis.
- Laboratory electrochemistry experiments (often in specific diameters like 1.6 mm and cut lengths like 70 mm).
- Electroplating baths (especially for precious metals and hard chrome plating).
- Advantages: High corrosion resistance, stable electrochemical performance, low overpotential, long operating life with minimal platinum consumption.
- Description: A titanium wire substrate precisely coated with a thin, adherent layer of pure platinum metal (Pt), typically 0.1 to 20 microns thick.
PP (Polypropylene) Coated Titanium Wire:
- Description: Consists of a titanium wire core insulated with a layer of polypropylene.
- Unique Feature: The PP coating provides electrical insulation, UV resistance, and low water permeability, protecting the titanium core in exposed or submerged environments. The coating can be color-coded (e.g., orange for anode wiring, blue for reference electrodes per some standards).
- Applications: Primarily used in Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) systems, particularly for discrete anode installations. The titanium wire serves as the conductor connecting the power source to the active anode element (which might be a different material), while the PP coating provides durable insulation along the wire run.
- Typical Specs: Diameter around 2.4 mm ± 0.1 mm.
- Advantages: Protects the titanium conductor from environmental degradation (UV, moisture), ensuring long service life in outdoor and wet applications.
Pure Titanium Wire (as Electrode or Component):
- Description: Standard titanium wire made from commercially pure grades or alloys.
- Unique Feature: Provides the fundamental properties of titanium in a flexible wire form. Can be used directly as an electrode where the bare titanium’s passive layer is sufficiently conductive or where the reactions occur efficiently on the bare surface under specific conditions.
- Applications:
- Used to hang or tie parts during chemical processing and anodizing where the wire itself acts as an electrode or conductor to the part being processed.
- Can serve as a base material for applying other coatings (like MMOs or specialized oxides, though less common as a wire product type compared to Pt or PP coatings) for specific wire electrode applications.
- Used in certain electrochemical setups where bare titanium is suitable.
Advantages of Titanium Wire Electrodes
Across its different forms, Titanium Electrode Wire offers compelling benefits:
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Fundamental to all types, ensuring durability in harsh chemical and marine environments.
- Stable Performance: Platinum coatings provide consistent electrochemical activity. PP coating provides stable insulation.
- Long Operating Life: Especially for coated types, designed for years of reliable use with minimal degradation.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Facilitates installation and provides structural integrity.
- Versatility: Adaptable to a wide range of electrochemical processes, laboratory setups, and industrial applications.
- Form Factor: The wire geometry is ideal for applications requiring flexibility, fine diameter, or specific cell configurations.
Partnering with an Expert Supplier
Selecting the right type of Titanium Electrode Wire, ensuring the correct titanium grade, precise diameter, and appropriate coating or insulation requires specialized knowledge. A manufacturer and supplier specializing in titanium and titanium oxide electrodes and materials possesses the necessary expertise in titanium wire drawing, coating technologies (Platinum, PP), and understanding the demands of various electrode applications.
Look for a partner who can offer:
- Expertise in different titanium grades and wire forms.
- Capability for precise and adherent coating application (Platinum, PP).
- Understanding of electrochemical requirements to advise on optimal wire type and specs.
- Rigorous quality control ensuring material properties and coating integrity meet standards.
- Customized production for specific diameters, lengths, coating thicknesses, or PP coating colors.
Collaborating with such an expert is crucial for obtaining high-quality Titanium Electrode Wire precisely suited to your specific needs.
Titanium Electrode Wire, in its various forms including pure titanium wire, Platinum Coated Titanium Wire Electrodes, and PP Coated Titanium Wire, is a versatile and high-performance material. Leveraging titanium’s exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, these wires are engineered with specific coatings or insulations to serve effectively in demanding applications such as electroplating, cathodic protection, chemical processing, laboratory electrochemistry, and welding. Their durability and adaptability make them essential components across a range of industries.
FAQs About Titanium Electrode Wire
What are the benefits of using platinum-coated titanium electrodes (wire form)?
Benefits include excellent corrosion resistance, high catalytic activity for electrochemical reactions, dimensional stability, long operating life with minimal platinum consumption, and adaptability into various shapes (as a wire).
How does the thickness of the platinum coating affect the performance of titanium electrodes (wire form)?
The platinum coating thickness directly impacts lifespan and cost. A thicker coating generally provides a longer service life by allowing more Pt to be consumed before the titanium substrate is exposed. However, thicker coatings increase the cost due to the high price of platinum. The optimal thickness is an engineering balance between desired life, performance, and budget.
What are the typical applications of titanium wire in the aerospace industry?
In the aerospace industry, titanium wire is primarily used as TIG welding rods for joining titanium airframe components, engine parts, and other critical structures due to titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue and corrosion.
How does the corrosion resistance of platinum-coated titanium wire compare to other materials?
Platinum-coated titanium wire offers superior corrosion resistance compared to many other electrode materials. The titanium base resists attack in aggressive environments, while the platinum coating provides protection against oxidation and chemical degradation where bare titanium might be challenged under anodic conditions. It is significantly more corrosion-resistant than materials like copper, steel, or even bare titanium in certain specific electrochemical environments.
What are the environmental benefits of using titanium electrodes (including wire forms) in water treatment?
Environmental benefits include being non-toxic (unlike lead electrodes), having a long service life which reduces waste generation, and enabling energy savings (due to low overpotential) compared to traditional electrodes, contributing to a lower carbon footprint for water treatment processes like electrochemical disinfection or oxidation.