Description
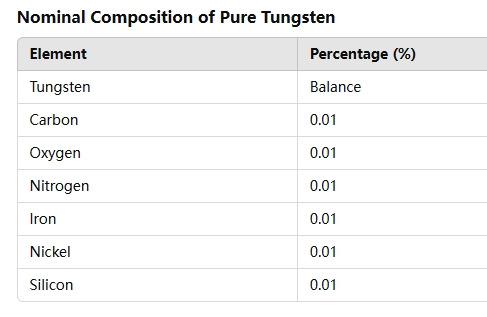
Pure Tungsten (W)

Introduction Tungsten is the refractory metal with the highest melting point, known for its high density and low thermal expansion coefficient. It maintains exceptional strength and good electrical resistivity even at extremely high temperatures. However, pure tungsten is very difficult to process and manufacture. Eagle Alloys offers finished tungsten parts with quick turnaround times and provides various tungsten alloys, including lanthanum-tungsten (1%, 1.5%, 2%) and thorium-tungsten and tungsten-rhenium (1%, 2%, 3%, 4%) alloys.
Properties
- Highest Melting Point: Superior among all refractory metals.
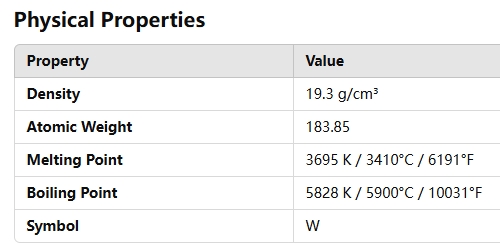
- High Density: 19.25 g/cm³, providing excellent mass and stability.
- Low Thermal Expansion: Minimizes deformation under temperature changes.
- Exceptional High-Temperature Strength: Maintains integrity at extreme temperatures.
- Good Electrical Resistivity: Efficient for electrical applications.
- Low Vapor Pressure: Enhances performance in high-temperature environments.
Alloys Offered
- Lanthanum-Tungsten Alloys: 1%, 1.5%, 2%
- Thorium-Tungsten Alloys: 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%
- Tungsten-Rhenium Alloys: Various compositions available
Applications
- High Vacuum Technology: Ideal for components requiring dimensional stability.
- Glass Seals and Furnace Structures: Utilized for their high melting points and structural strength.
- Radiation Shielding: High density effectively absorbs radioactive radiation.
- Steel Additives: Enhances the physical properties of steel.
- High-Density Alloys: Combined with nickel, copper, and iron for machinable, high-density materials.
- Lighting Industry: Long-used for filaments due to its high strength at elevated temperatures.
- Heating Elements: Preferred for vacuum furnaces and other heating applications that exceed the performance of molybdenum and tantalum.
Advantages
- Superior High-Temperature Strength: Outperforms other refractory metals in extreme conditions.
- High Density and Thermal Stability: Essential for applications demanding mass and stability.
- Versatile Alloying Options: Customizable properties to meet specific industry needs.
Typical Applications
- Medical Equipment
- Filaments
- X-Ray Targets
- Vacuum Furnaces
- Ion Implantation Components
- Electrical Contacts
- Heating Coils and Heating Elements for Electric Furnaces
- Glass-Metal Seals
- Sputtering Targets
- Supports and Insulating Shields
- Electrodes, Cathodes, and Anodes
- Thermal Bodies
- Electronics
- Tungsten Ribs and Crucibles
- Radiation Shielding
Standards
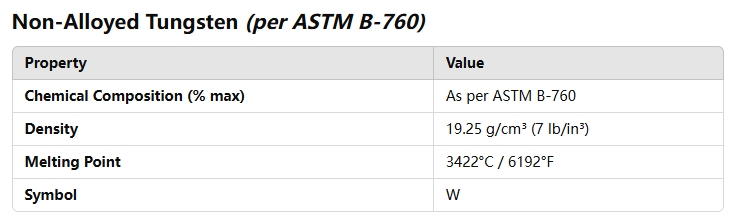
- ASTM B-760
- AMS 7897
- AMS 7898 Series
- ASTM F-288 Type






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.